M Diop, M El-Hayek, J Attard, A Muhieddine, V Veremeienko, S Soorkia, Ph Carbonnière, A de la Lande, B Soep, N Shafizadeh. J. Chem. Phys. 2023, 159, 194308. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0174351. Link for full text in HAL.
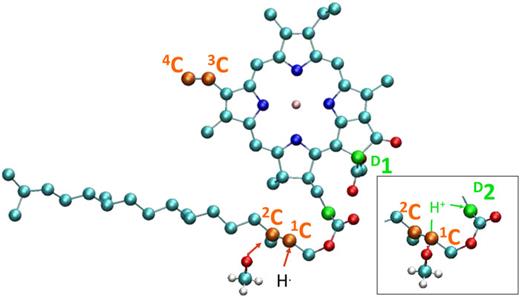
Pheophytin a and chlorophyll a have been investigated by electrospray mass spectrometry in the positive and negative modes, in view of the importance of the knowledge of their properties in photosynthesis. Pheophytin and chlorophyll are both observed intensely in the protonated mode, and their main fragmentation route is the loss of their phytyl chain. Pheophytin is observed intact in the negative mode, while under collisions, it is primarily cleaved beyond the phytyl chain and loses the attaching propionate group. Chlorophyll is not detected in normal conditions in the negative mode, but addition of methanol solvent molecule is detected. Fragmentation of this adduct primarily forms a product (−30 amu) that dissociates into dephytyllated deprotonated chlorophyll. Semi-empirical molecular dynamics calculations show that the phytyl chain is unfolded from the chlorin cycle in pheophytin a and folded in chlorophyll a. Density functional theory calculations have been conducted to locate the charges on protonated and deprotonated pheophytin a and chlorophyll a and have found the major location sites that are notably more stable in energy by more than 0.5 eV than the others. The deprotonation site is found identical for pheophytin a and the chlorophyll a-methanol adduct. This is in line with experiment and calculation locating the addition of methanol on a double bond of deprotonated chlorophyll a.